Day-1 Introduction to Software Testing, Back Box and White Box Testing
Day-2 Software Testing Types and SDLC
Day-3 Software Development Models (Waterfall and V-Model)
Day-4 Software Development Models (RAD & Agile Model)
Day-5 Software Testing Life Cycle (STLC)
Day-6 Manual & Automation Testing
Day-7 Unit, Integration & System Testing
Day-8 Smoke-Sanity and Regression Testing
Day-9 Non-functional Testing
Day-10 Test Case Design
Day-11 Database Testing
Day-12 JIRA & Bugzilla Tools
Day-13 SOAP UI and Mobile Testing
Day-14 QTP/UFT
Day-15 Selenium & QC
Day-16 Interview Questions
Day-1 Introduction to Software Testing, Back
Box and White Box Testing
Q.
What is Software Testing?
A. It
is an activity to check whether the actual result matched the expected results
and also to ensure that the software is Defect(bug) free.
It also helps to identify errors, gaps or missing requirements as compare to the actual requirements.
Software Testing can be done manually or by using Automation tools(e.g. QTP, Selenium etc)
Q. What is the difference between Black Box and White Box Testing?
A.
Black Box Testing
When the testing is done without looking the internal Code Structure, Implementation Details and knowledge about how it is actually implemented, is called as Black Box Testing.
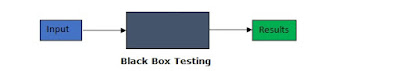 E.g.
Input --> 2, 3
Function --> ADD
Output --> 5
Here we are not sure about the internal logic ADD is written to calculate the sum of 2 input values.
So In this Type of testing, the main focus is based on validation of functional requirements. We can also do the testing between the modules using the Black Box testing. The tools like QTP, Selenium, Load Runner, J Meter etc can be used for Black Box Testing.
E.g.
Input --> 2, 3
Function --> ADD
Output --> 5
Here we are not sure about the internal logic ADD is written to calculate the sum of 2 input values.
So In this Type of testing, the main focus is based on validation of functional requirements. We can also do the testing between the modules using the Black Box testing. The tools like QTP, Selenium, Load Runner, J Meter etc can be used for Black Box Testing.
White Box Testing
To Validate the internal structure and comparing the results is called as White Box Testing.
E.g.
Input --> 2, 3
Function --> ADD( Input 1+Input 2)
Output --> 5
Here the ADD function reveals that the sum is done by adding the 2 inputs.
For White Box Testing, Programming Knowledge is must.
Using White Box Testing, Testing can be done for limited part of application.
Day-2 Software Testing Types and SDLC
Q. Types of Software Testing?
A. There are 3 major categories of Software Testing:
Q. What is SDLC (Software Development Life Cycle)?
A. The sequence of Activities done to develop complete software is called as Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC).
There are 5 major phases of SDLC:
Phase 1 - Requirement Analysis Phase
Phase 2 - Design Phase - High Level and Low Level Design
Phase 3 - Coding Phase
Phase 4 - Testing Phase
Phase 5 - Implementation Phase
Requirement Analysis Phase:- In this phase of Software Development Life Cycle, gathering and analyzing of the requirements is done using various resources like via client interaction, SRS (Software Requirement Specification) etc.
Design Phase:- This phase of SDLC consists of architecture and design of the software which is going to be implemented. In this phase, the decision making of programming language, database, 3rd party software's gets decided.
High Level Design is mainly the Architecture of the software which includes the interaction with the external components.
Low Level Design is the software structure/design and the interaction between the internal components, layers etc.
Coding Phase:- In this phase, actual code of the software is done by the developer.
Testing Phase:- All the testing activities like preparing Test Case Plan, Test Cases, Execution of Test Cases are done under this phase of SDLC.
Implementation Phase:- Once the software is completed, the implementation/deployment is done at the client's actual environment under this phase. After this phase, the software goes live s that the end user can use it.
Day-3 Software Development Models (Waterfall and
V-Model)
Q. What are software
development Models?
A. To
perform the SDLC activities, there are various models used in developing the software.
a.
Waterfall Model: This is the sequential model where each phase of SDLC divided into
different activities. The next phase will start only after completion of
previous phase.

This model is good approach when
the software application is small and all the requirements are fixed and given
in the requirement stage. But for the large software’s, if the requirements are
missed and comes in the later stages of development, it is very difficult to
accommodate them. Also if any requirement is misunderstood then it’s very
difficult to correct. If the requirement is wrong then wrong design and then
wrong coding and implementation. Making serious mistakes in design and
architecture of software can lead to redesign the entire software. So this
model is not preferable to build large applications.
b.
V-Model: This is an extension of
waterfall model where each phase of SDLC is parallel executed with testing.
There is a corresponding testing phase with each of development phase.
Day-4 Software Development Models (RAD & Agile
Model)
c.
RAD (Rapid Application Development) Model: This is one of the iterative
models of software development where the development of each phase of SDLC is
done in parallel.
By using RAD model, a component (part of application)
as a prototype is developed as a whole including testing and then this component
is used in the main software. Continuous integration and rapid delivery is the
main advantage of this model.
d.
Agile Model: This is one of model for the
developing the software in iterative and incremental mode. Each of the
activities of Software development is done in parallel.
This model’s main focus is process
adaptability and customer satisfaction by rapid delivery of working
software. Agile Methods break the product into small incremental
builds. These builds are provided in iterations. Each iteration has the set of
work which is done and deployed to live environment.
There are various methodologies
to implement Agile and the most popular methodology is Scrum.
Day-5 Software Testing Life Cycle (STLC)
Q. What is STLC (Software
Testing Life Cycle)?
A. The Series of activities done by Testers
to test software product is called as STLC (Software Testing Life
Cycle).
There are various stages of Software
Testing Life Cycle:-

Requirement
Analysis: To identify testable requirements. QA Team can interact
with Client, Business Analyst, Technical Leads, and System Architects etc to
understand the requirements in detail. The requirements can be functional or
non-functional.
In this phase, Software
Traceability Matrix (document to map user requirements with the test cases)
is prepared.
Test
Planning: Test Strategy and Test Plan is determined under this
stage. This is the document which includes- Types Of testing, test tools
selection, test effort estimation, resource planning, training requirements
etc.
Test
Case Development: In this phase of STLC, the activities like
creation, verification and rework of test cases & test scripts. Test data
is also identified/created and is reviewed and then reworked as well under this
stage.
Environment
Setup: This can be done with Test Case Development Stage. The
major activities performed under this stage are – preparation of hardware and
software requirement list for the Test Environment, Setup test Environment and
test data and performing the smoke test on the build provide for testing.
Test
Execution: In this phase of STLC, the testers carry out
the testing based on the test plans and the test cases prepared in earlier
stage. If there are bugs then they gets reported back to the development team
for correction and retesting will be performed once the bugs are fixed. In this
stage, the tester also Document test results, and log defects for failed cases
and track the defect to closure.
Test Cycle Closure: This is not the actual phase of STLC but important to
have under the testing life cycle. In this stage, the testing team Evaluate
cycle completion criteria based on Time, Test coverage, Cost, Software, Critical
Business Objectives, and Quality, Test result Analysis and prepare the Test
matrix.
Day-6 Manual & Automation Testing
Q. What is Manual
Testing?
A. It is a Software Testing where Testers manually
execute test cases without using any automation tools.
The main goal of Manual Testing is:-
è To ensure the
application is error free and covering the specified functional requirements.
è Test cases
having 100% test coverage.
è Making sure that reported
defects are fixed by developers and re-testing has been performed by testers on
the fixed defects.
Q. What is Automation
Testing? Why Automation Testing?
A. Automation
Testing is a process where the testing is performed using tools rather than by
human. The main goal of Automation Testing is to reduce the number of manual test
cases which are required to run repeatedly.
By using a test automation
tool, we can record the test suite and then re-play whenever it is required.
Q. What is Automation
Testing Process?
A. There are 5 major steps for
Automation Process:-Q. What are the main Automation
Testing Tools?
A. There are many automation testing
tools in the market but below are most popular:
·
Selenium- For Regression Testing
·
QTP (MicroFocus UFT) - For Functional & Regression Testing
Q. When to use Automation
Testing?
A. Automated testing is suited for
Regression Testing, Performance Testing, Load Testing or highly repeatable
functional test cases.
Day-7 Unit, Integration & System Testing
Q. What is Unit Testing?
Why Unit testing required?
A.
Testing part of application in
isolation to verify whether it’s correct or not, using code is called as Unit
Testing.
The goal of Unit
Testing is to isolate each part of the program and show that the individual
parts are correct. Unit testing is usually performed by the developer.
Unit testing can be automated using Automation Test
Frameworks like nUnit, JTest, JUnit etc.
Q. What is Integration Testing?
What are the different approaches of Integration Testing?
A. Testing a
group of logically integrated Individual modules is called as Integration
Testing. Integration testing mainly focuses on the data communication between
the modules.
Integration testing also called
as ‘Integration & Testing’, ‘Thread Testing’ and ‘String Testing’.
Integration
Testing Approaches:
1. Big Bang
Approach
2. Incremental
Approach
·
Top-Down
Approach
·
Bottom-Up
Approach
·
Sandwich
Approach - Combination of Top Down and Bottom Up
1. Big Bang Approach: In this approach, all the modules
are integrated together at once and then testing is performed.
This approach is good for the small applications.
2. Incremental Approach: In this approach, testing is done
between logically related modules. This process continues till all the modules
are joined and tested.
·
Top-Down Approach: In this approach, testing
takes place from top to down modules. So here critical modules are tested on
priority so if there is any design flaw, it can be fixed at the early stage.

·
Bottom-Up Approach: In this approach, testing
is done from the bottom modules and then by joining the top modules.

Q. What is the
procedure for Integration Testing?
A. Below is
the steps/procedure for integration testing:-
Step#1: Preparation
of Integration Tests Plan
Step#2: Design
the Test Cases, Scenarios and Scripts.
Step#3: Executing
the test Cases
Step#4: Reporting
the defects.
Step#5: Tracking
& re-testing the defects after fixed by the developer.
Step#6: Steps
3, 4 & 5 are repeated until the completion of Integration is successful.
Q. What is System Testing?
A. Testing
of a complete and fully integrated software product is called as System
Testing. System
test falls under the black box testing category of software testing. System Testing is actually
a series of different tests whose sole purpose is to exercise the full computer
based system. System Testing involves testing the software code for following:-
·
Testing the
fully integrated applications including external peripherals in order to
check how components interact with one another and with the system as a whole.
This is also called End to End testing scenario.
·
Verify
thorough testing of every input in the application to check for desired
outputs.
·
Testing of
the user's experience with the application.
Q. What is Software Testing
Hierarchy?
A.
Q. What are different
types of System Testing?
A. Below
are types of System Testing:-
·
Usability Testing
·
Load Testing
·
Regression Testing
·
Recovery Testing
·
Migration Testing
·
Functional Testing
· Hardware/Software Testing
Day-8 Smoke-Sanity and Regression Testing
Q. What
is Smoke and Sanity testing? How they are different?
A. Smoke testing addresses the
critical functionality testing while the Sanity testing addresses the new
functionality testing.
Smoke testing is done on
the unstable builds while Sanity testing is done under the stable builds.
Q. What
is Regression Testing? What are the automation tools can be used for regression
testing?
A. Regression Testing is defined as a
type of software testing to confirm that a recent program or code change has
not adversely affected existing features.
Re-executing of fully or
partially executed tests is called as Regression testing.
Regression testing is done to
ensure that the old code still work well while the new code is added.
For Regression Testing, Selenium (for
browser based regression testing) and QTP(Data driven, Keyword based tool) are
widely used.
Q. What
is the difference between Re-Testing and Regression Testing?
A. Testing the functionality
or bug again to ensure the code is fixed is called as Re-Testing. If the bug is
not fixed, Defect needs to be re-opened and if it is fixed, Defect is
closed.
While in Regression testing, testing of the software
application is done when there is some code change and making it ensure that
the new code has not affected other parts of the software.
Day-9 Non-functional Testing
Q. What
is Non-functional Testing? What are the parameters for Non-functional testing?
A. Non-functional testing is a type
of testing to check non-functional aspects (performance, usability,
reliability, portability etc) of a software application.
E.g. Performance
testing on Number of users login at a time
Below are the main parameters which can be the
part of non-functional testing:- Q. What
is Non-functional Testing Types?
A. There
are more than 100 types of Non-functional testing but below are main:-
·
Performance Testing
·
Load Testing
·
Fail-over Testing
·
Security Testing
·
Compatibility Testing
·
Usability Testing
·
Stress Testing
·
Maintainability Testing
·
Scalability Testing
·
Volume Testing
·
Security Testing
·
Disaster Recovery Testing
·
Compliance Testing
·
Usability Testing
·
Portability Testing
·
Efficiency Testing
·
Reliability Testing
·
Baseline Testing
·
Endurance Testing
·
Documentation Testing
·
Recovery Testing
·
Internationalization Testing
·
Localization Testing
Day-10 Test Case Design
Q. What
is Test Case? What is the difference between Test Case and Test Scenario?
A. A set of actions executed to verify a
particular feature or functionality of your software application is called as
Test Case.
Test
Scenario covers the wide range of possibilities while the Test Case covers a single feature or
functionality.
Q. What
is the format of a Standard Test Case?
A. Below is
the format of a Standard Test Cases:-

Q. What are
the best practices to write a good Test Case?
A. Below
are the best practices to write good test case:
·
Simple and transparent
– Test case should be easy with test steps
·
Keeping End User in
Mind
·
Avoid repetition
·
Do not assume
·
Ensure 100% Coverage -
Use Traceability
Matrix to ensure no functions/conditions is left untested
·
Test Cases must be
identifiable – test case should have id
·
Implement Testing Techniques-
Like Boundary Value Analysis, Equivalence Partition, State Transition
Technique, And Error Guessing Technique etc.
·
Self cleaning-
Configuration Testing
·
Repeatable and self-standing
·
Peer Review
Day-11 Database Testing
Q. What
is Database Testing? What are the types of Database Testing?
A. To check the schema, tables,
triggers, etc. of the database under test is called as Database Testing. It can
include creating queries to load the data, stress test and check the
responsiveness of the data
Database testing also checks data integrity and consistency
for the data in database.
So Database testing includes validating the schema,
database tables, columns, keys and indexes, stored procedures, triggers,
database server validations, validating data duplication etc.
The
database Testing can be classified in to 3 types:
1.
Structural Testing
2.
Functional Testing
3.
Non-functional Testing
Structural Database Testing includes the validating
the data repository elements which are not allowed to be manipulated by the end
user. So the tester has to write the Sql queries to perform this type of
database testing.
E.g.
·
Schema Mapping between the front end and back-end fields
·
Table column compatibility like Data Type, Length etc. in
front-end and back-end
·
Checking the validity of Primary and Foreign keys
·
Validating the naming convention of the keys and indexes.
·
Checking the coding standard of stored procedure scripts- Error
Handling.
·
Trigger Testing validation
Functional Database Testing talks about ensuring
the transactions and operations performed by the end users are consistent with
the requirement specifications.
E.g.
·
Allow NULL value for mandatory field
·
Size of each column field is sufficient?
·
Name of the same column field in all tables
·
Checking the computation field in the database
Performance Testing = Load Testing + Stress Testing
The main Load & Stress testing
Tools are - load runner, win runner and JMeter
Q. What
is joins in Database. What are the different types of joins in Sql Server
Database?
A. Combining
or joining 2 or more tables to achieve the desired results is called as Join.
In Sql Server, there are mainly 4 types of joins:
·
Natural Join/Simple Join- Equi Join and Non-Equi Join
·
Inner Join
·
Outer Join – Left Outer Join, Right Outer Join and Full Join
·
Cross Join – Cross Product of 2 tables
·
Self Join – Joining the table to itself
Day-12 JIRA & Bugzilla Tools
Q. What is JIRA?
A. JIRA is a tool developed by Australian Company Atlassian and used
for Bug Tracking, Issue Tracking, and Project Management.
The basic use of this tool is to
track issue and bugs related to the software and Mobile apps. This tool is also used for Project Management.
Q. What is JIRA Scheme?
A. The Configurable section of JIRA called as JIRA Scheme. This configurable
section contains:
·
Workflows

·
Issue Types – Once the Project imported, issues can be created under the project.
Issues types can be Bug, Feature, Epic, Story, Task, Sub-Task, Enhancement etc.
·
Custom Fields
·
Screens - Display of field in JIRA is known as a screen
·
Field
Configuration
·
Notification
·
Permissions
Q. What is JIRA Dashboard? What all the
features contain sin JIRA Dashboard.
A. JIRA Dashboard contains many features like below:
Q. What is JIRA Component?
A. Components
are sub-sections of a project; they are used to group issues within a project
into smaller parts. Components add some structures to the projects, breaking it
up into features, teams, modules, sub-projects and more. Using components, you
can generate reports, collect statistics, and display it on dashboards and so
on.

Q. What are Issue Attributes in JIRA?
A.
The Issue Attribute comprises of:
·
Statuses - To do, In-Progress,
Open, Closed, Re-Opened, and Resolved
·
Resolutions - Fixed, Won't fix,
Duplicate, Incomplete, Cannot reproduce, Done
·
Priorities - Critical, major, minor, blocker and Trivial.
Q. How to Create an issues in JIRA?
A.
There are the steps to create a
new issue in JIRA:
Step#1:
Select Project Type

Step#2: After clicking the Next, another screen will open
and will require entering the details below:

Step#3: After submit button clicked, a window will open the
enter the issue details

Step#4: After clicking Create Button, a popup message will display
as below:

Q. What are Reports in JIRA? What is
Burn-down Chart?
A. There are various reports used in JIRA Agile like Sprint Report, Epic Report, Version
Report, Velocity Chart, Control Chart, Cumulative flow diagram but the main
report is Burn-Down chart report. Burn-down Chart shows the
actual and estimated amount of work to be done in the sprint.

Q. What is Bugzilla? What all the key
features of Bugzilla.
A. Bugzilla is a Defect tracking tool, however, it can be used as a test management tool as such
it can be easily linked with other Test Case management tools like Quality Center (QC), Test link etc.
Key features of Bugzilla
includes
·
Advanced search
capabilities
·
E-mail
Notifications
·
Modify/file
Bugs by e-mail
·
Time tracking
·
Strong security
·
Customization
·
Localization
Q. What are the steps to create Bug
Report in Bugzilla?
A. Below are the steps needs to follow when creating bug report using Bugzilla:
Step#1: Login with new/existing account.
Step#2: To create a new bug in
Bugzilla, visit the home-page of Bugzilla and click
on NEW tab from the main menu
Day-13 SOAP UI and Mobile Testing
Q. What is SOAP UI? What is the use of
SOAP UI tools?
A. SoapUI is one of the API Testing Tool. By using SOAPUI, we can do
functional, load, security and compliance tests on your API.
Q. What is Web Service? Why Web Service
is needed?
A.
Day-14 QTP/UFT
Day-15 Selenium & QC
Day-16 Interview Questions & Answers
